Table of Contents
So far, this book has focused on the basics of simple yet effective network solutions. Network administrators who take pride in their work (that's most of us, right?) take care to deliver what our users want, but not too much more. If we make things too complex, we confound our users and increase costs of network ownership. A professional network manager avoids the temptation to put too much pizazz into the way that the network operates. Some creativity is helpful, but do keep it under control.
Five years ago there were two companies from which a lesson can be learned. In one case the network administrator spent three months building a new network to replace an old Netware server. What he delivered had all the bells and whistles he could muster. There were a few teething problems during the change-over, nothing serious but a little disruptive all the same. Users were exposed to many changes at once. The network administrator was asked to resign two months after implementing the new system. This was necessary because so many staff had complained they had lost time and were not happy with the new network. Everything was automated and he delivered more features than any advanced user could think of. He was just too smart for his own good.
In the case of the other company, a new network manager was appointed to oversee the replacement of a LanTastic network with an MS Windows NT 4.0 network. He had the replacement installed and operational within two weeks. Before installation and change-over, he called a meeting to explain to all users what was going to happen, how it would affect them and that he would be available 24 hours a day to help them transition. One week after conversion, he held another meeting asking for cooperation in the introduction of a few new features that would help to make life easier. Network users were thrilled with what he was doing to help them. The network he implemented was nowhere near as complex as the first example, had fewer features, and yet he had happy users. Months later he was still adding new innovations. He always asked the users if a particular feature was what they wanted. He asked his boss for a raise and got it. He often told me, “Always keep a few new tricks up your sleeves for when you need them.” Was he smart? You decide. Let's get on with our next exercise.
Abmas Accounting Inc. has grown. Mr. Meany likes you and says he knew you were the right person for the job. That's why he asked you to install the new server. The past few months have been hard work. You advised Mr. Meany that it is time for a change. Abmas now has 52 users, having acquired an investment consulting business recently. The new users were added to the network without any problems.
Some of the Windows clients are getting to be past their use-by date. You have found damaged and unusable software on some of the workstations that came with the acquired business and found some machines that are in need of both hardware and software maintenance.
Mr. Meany has decided to retire in 12 months. He wants you to help him make the business run better. Many of the new staff want notebook computers. They visit customer business premises with the need to use local network facilities; these users are technically competent. The company uses a business application that requires Windows XP Professional. In short, a complete client upgrade is about to happen. Mr. Meany told you that he is working on another business acquisition and that by the time he retires there will be 80 to 100 users.
Mr. Meany is not concerned about security. He wants to make it easier for staff to do their work. He has hired you to help him appoint a full-time network manager before he retires. Above all, he says he is investing in the ability to grow. He is determined to live his lifelong dream and hand the business over to a bright and capable executive who can make things happen. This means your network design must cope well with growth.
In a few months, Abmas will require an Internet connection for email and so staff easily obtain software updates. Mr. Meany is warming up to the installation of anti-virus software, but is not yet ready to approve this expense. He told you to spend the money a virus scanner costs on better quality notebook computers for mobile users.
One of Mr. Meany's golfing partners sold him on the idea to buy new laser printers. One black only, the other a color laser printer. Staff support the need for a color printer so they can present more attractive proposals and reports.
Mr. Meany also asked if it would be possible for one of the staff to manage user accounts from the Windows desktop. That person will be responsible for basic operations.
What are the key requirements in this business example? A quick review indicates a need for:
In this instance the installed Linux system is assumed to be a Red Hat Linux Fedora Core2 server (as in ???).
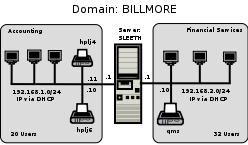
It is time to implement a domain security environment. You will use the smbpasswd (default) backend. You should implement a DHCP server. There is no need to run DNS at this time, but the system will use WINS. The Domain name will be BILLMORE. This time, the name of the server will be SLEETH.
All printers will be configured as DHCP clients. The DHCP server will assign the printer a fixed IP address by way of its Ethernet interface (MAC) address. See ???.
Note
The smb.conf file you are creating in this exercise can be used with equal effectiveness with Samba-2.2.x series releases. This is deliberate so that in the next chapter it is possible to start with the installation that you have created here, migrate it to a Samba-3 configuration and then secure the system further. Configurations following this one will utilize features that may not be supported in Samba-2.2.x releases. However, you should note that the examples in each chapter start with the assumption that a fresh new installation is being effected.
Later on, when the Internet connection is implemented, you will add DNS as well as other enhancements. It is important that you plan accordingly.
You have split the network into two separate areas. Each has its own ether-switch. There are 20 users on the accounting network and 32 users on the financial services network. The server has two network interfaces, one serving each network. The network printers will be located in a central area. You plan to install the new printers and keep the old printer in use also.
You will provide separate file storage areas for each business entity. The old system will go away, accounting files will be handled under a single directory, and files will be stored under customer name, not under a personal work area. Staff will be made responsible for file location, so maintain the old share point.
Given that DNS will not be used, you will configure WINS name resolution for UNIX hostname name resolution.
It is necessary to map Windows Domain Groups to UNIX groups as a minimum. It is advisable to also map Windows Local Groups to UNIX groups. Additionally, the two key staff groups in the firm are Accounting Staff and Financial Services Staff. For these, it is necessary to create UNIX groups as well as Windows Domain Groups.
In the sample smb.conf file, you have configured Samba to call the UNIX groupadd to add group entries. This utility does not permit the addition of group names that contain upper-case characters or spaces. This is considered a bug. The groupadd is part of the shadow-utils Open Source Software package. A later release of this package may have been patched to resolve this bug. If your operating platform has this bug, it means that attempts to add a Windows Domain Group that has either a space or upper-case characters in it will fail. See TOSHARG, Section 11.3.1, Example 11.1, for more information.
Vendor-supplied printer drivers will be installed on each client. The CUPS print spooler on the UNIX host will be operated in raw mode.
Mr. Meany is an old-school manager. He sets the rules and wants to see compliance. He is willing to spend money on things he believes are of value. You need more time to convince him of real priorities.
Go ahead, buy better notebooks. Wouldn't it be neat if they happened to be supplied with anti-virus software? Above all, demonstrate good purchase value and remember to make your users happy.
In this example, the assumption is made that this server is being configured from a clean start. The alternate approach could be to demonstrate the migration of the system that is documented in ??? to meet the new requirements. The decision to treat this case, as with future examples, as a new installation is based on the premise that you can determine the migration steps from the information provided in the separate chapter on this subject. Additionally, a fresh installation makes the example easier to follow.
Each user will be given a home directory on the UNIX system, which will be available as a private share. Two additional shares will be created, one for the Accounting Department and the other for the Financial Services Department. Network users will be given access to these shares by way of group membership.
UNIX group membership is the primary mechanism by which Windows Domain users will be granted rights and privileges within the Windows environment.
The user alanm will be made the owner of all files. This will be preserved by setting the sticky bit (set UID/GID) on the top-level directories.
Using UNIX/Linux system tools, name the server sleeth.
Place an entry for the machine sleeth in the /etc/hosts. The printers are network attached, so it is desirable that there should be entries for the network printers also. An example /etc/hosts file is shown here:
192.168.1.1 sleeth sleeth1 192.168.2.1 sleeth2 192.168.1.10 hplj6 192.168.1.11 hplj4 192.168.2.10 qms
Install the Samba-3 binary RPM from the Samba-Team FTP site.
Install the ISC DHCP server using the UNIX/Linux system tools available to you.
Given that Samba will be operating over two network interfaces and clients on each side may want to be able to reach clients on the other side, it is imperative that IP forwarding shall be enabled. Use the system tool of your choice to enable IP forwarding. In the absence of such a tool on the Linux system, add to the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file an entry as follows:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
This causes the Linux kernel to forward IP packets so that it acts as a router.
Install the smb.conf file as shown in ??? and ???. Combine these two examples to form a single /etc/samba/smb.conf file.
Add the user root to the Samba password backend:
root# smbpasswd -a root New SMB password: XXXXXXX Retype new SMB password: XXXXXXX root#
This is the Windows Domain Administrator password. Never delete this account from the password backend after Windows Domain Groups have been initialized. If you delete this account, your system is crippled. You cannot restore this account and your Samba server is no longer capable of being administered.
Create the username map file to permit the root account to be called Administrator from the Windows network environment. To do this, create the file /etc/samba/smbusers with the following contents:
#### # User mapping file #### # File Format # ----------- # Unix_ID = Windows_ID # # Examples: # root = Administrator # janes = "Jane Smith" # jimbo = Jim Bones # # Note: If the name contains a space it must be double quoted. # In the example above the name 'jimbo' will be mapped to Windows # user names 'Jim' and 'Bones' because the space was not quoted. ####################################################################### root = Administrator #### # End of File ####
Create and map Windows Domain Groups to UNIX groups. A sample script is provided in ???. Create a file containing this script. We called ours /etc/samba/initGrps.sh. Set this file so it can be executed, and then execute the script. Sample output should be as follows:
Example 3.1. Script to Map Windows NT Groups to UNIX Groups
#!/bin/bash # # initGrps.sh # # Create UNIX groups groupadd acctsdep groupadd finsrvcs # Map Windows Domain Groups to UNIX groups net groupmap modify ntgroup="Domain Admins" unixgroup=root net groupmap modify ntgroup="Domain Users" unixgroup=users net groupmap modify ntgroup="Domain Guests" unixgroup=nobody # Add Functional Domain Groups net groupmap add ntgroup="Accounts Dept" unixgroup=acctsdep type=d net groupmap add ntgroup="Financial Services" unixgroup=finsrvcs type=d
root# chmod 755 initGrps.sh root# cd /etc/samba root# ./initGrps.sh Updated mapping entry for Domain Admins Updated mapping entry for Domain Users Updated mapping entry for Domain Guests No rid or sid specified, choosing algorithmic mapping Successfully added group Accounts Dept to the mapping db No rid or sid specified, choosing algorithmic mapping Successfully added group Domain Guests to the mapping db root# cd /etc/samba root# net groupmap list | sort Account Operators (S-1-5-32-548) -> -1 Accounts Dept (S-1-5-21-194350-25496802-3394589-2003) -> acctsdep Administrators (S-1-5-32-544) -> -1 Backup Operators (S-1-5-32-551) -> -1 Domain Admins (S-1-5-21-194350-25496802-3394589-512) -> root Domain Guests (S-1-5-21-194350-25496802-3394589-514) -> nobody Domain Users (S-1-5-21-194350-25496802-3394589-513) -> users Financial Services (S-1-5-21-194350-25496802-3394589-2005) -> finsrvcs Guests (S-1-5-32-546) -> -1 Power Users (S-1-5-32-547) -> -1 Print Operators (S-1-5-32-550) -> -1 Replicators (S-1-5-32-552) -> -1 System Operators (S-1-5-32-549) -> -1 Users (S-1-5-32-545) -> -1
For each user who needs to be given a Windows Domain account, make an entry in the /etc/passwd file as well as in the Samba password backend. Use the system tool of your choice to create the UNIX system accounts and use the Samba smbpasswd program to create the Domain user accounts.
There are a number of tools for user management under UNIX. Commonly known ones include: useradd, adduser. In addition to these, there are a plethora of custom tools. With the tool of your choice, create a home directory for each user.
Using the preferred tool for your UNIX system, add each user to the UNIX groups created previously as necessary. File system access control will be based on UNIX group membership.
Create the directory mount point for the disk sub-system that is mounted to provide data storage for company files. In this case the mount point indicated in the smb.conf file is /data. Format the file system as required, mount the formatted file system partition using mount, and make the appropriate changes in /etc/fstab.
Create the top-level file storage directories are follows:
root# mkdir -p /data/{accounts,finsvcs} root# chown -R root.root /data root# chown -R alanm.accounts /data/accounts root# chown -R alanm.finsvcs /data/finsvcs root# chmod -R ug+rwx,o+rx-w /dataEach department is responsible for creating its own directory structure within its share. The directory root of the accounts share is /data/accounts. The directory root of the finsvcs share is /data/finsvcs.
Configure the printers with the IP addresses as shown in ???. Follow the instructions in the manufacturers' manuals to permit printing to port 9100. This allows the CUPS spooler to print using raw mode protocols.
Configure the CUPS Print Queues as follows:
root# lpadmin -p hplj4 -v socket://192.168.1.11:9100 -E root# lpadmin -p hplj6 -v socket://192.168.1.10:9100 -E root# lpadmin -p qms -v socket://192.168.2.10:9100 -E
This creates the necessary print queues with no assigned print filter.
Edit the file /etc/cups/mime.convs to uncomment the line:
application/octet-stream application/vnd.cups-raw 0 -
Edit the file /etc/cups/mime.types to uncomment the line:
application/octet-stream
Using your favorite system editor, create an /etc/dhcpd.conf with the contents as shown in ???.
Example 3.2. Abmas Accounting DHCP Server Configuration File /etc/dhcpd.conf
default-lease-time 86400; max-lease-time 172800; default-lease-time 86400; option ntp-servers 192.168.1.1; option domain-name "abmas.biz"; option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.1, 192.168.2.1; option netbios-name-servers 192.168.1.1, 192.168.2.1; option netbios-node-type 8; ### NOTE ### # netbios-node-type=8 means set clients to Hybrid Mode # so they will use Unicast communication with the WINS # server and thus reduce the level of UDP broadcast # traffic by up to 90%. ############ subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { range dynamic-bootp 192.168.1.128 192.168.1.254; option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; option routers 192.168.1.1; allow unknown-clients; host hplj4 { hardware ethernet 08:00:46:7a:35:e4; fixed-address 192.168.1.10; } host hplj6 { hardware ethernet 00:03:47:cb:81:e0; fixed-address 192.168.1.11; } } subnet 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { range dynamic-bootp 192.168.2.128 192.168.2.254; option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; option routers 192.168.2.1; allow unknown-clients; host qms { hardware ethernet 01:04:31:db:e1:c0; fixed-address 192.168.1.10; } } subnet 127.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 { }Use the standard system tool to start Samba and CUPS and configure them to start automatically at every system reboot. For example:
root# chkconfig dhpc on root# chkconfig smb on root# chkconfig cups on root# /etc/rc.d/init.d/dhcp restart root# /etc/rc.d/init.d/smb restart root# /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups restart
Configure the Name Service Switch (NSS) to handle WINS based name resolution. Since this system does not use a DNS server, it is safe to remove this option from the NSS configuration. Edit the /etc/nsswitch.conf file so that the hosts: entry looks like this:
hosts: files wins
Example 3.3. Accounting Office Network smb.conf File [globals] Section
Example 3.4. Accounting Office Network smb.conf File Services and Shares Section
Does everything function as it ought? That is the key question at this point. Here are some simple steps to validate your Samba server configuration.
If your smb.conf file has bogus options or parameters, this may cause Samba to refuse to start. The first step should always be to validate the contents of this file by running:
root# testparm -s Load smb config files from smb.conf Processing section "[homes]" Processing section "[printers]" Processing section "[netlogon]" Processing section "[accounts]" Processing section "[service]" Loaded services file OK. # Global parameters [global] workgroup = BILLMORE passwd chat = *New*Password* \ %n\n *Re-enter*new*password* %n\n *Password*changed* username map = /etc/samba/smbusers syslog = 0 name resolve order = wins bcast hosts printcap name = CUPS show add printer wizard = No add user script = /usr/sbin/useradd -m '%u' delete user script = /usr/sbin/userdel -r '%u' add group script = /usr/sbin/groupadd '%g' delete group script = /usr/sbin/groupdel '%g' add user to group script = /usr/sbin/usermod -G '%g' '%u' add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -s /bin/false -d /var/lib/nobody '%u' logon script = scripts\logon.bat logon path = logon drive = X: domain logons = Yes preferred master = Yes wins support = Yes printing = cups ... ### Remainder cut to save space ###The inclusion of an invalid parameter (say one called dogbert) would generate an error as follows:
Unknown parameter encountered: "dogbert" Ignoring unknown parameter "dogbert"
Clear away all errors before proceeding and start or restart samba as necessary.
Check that the Samba server is running:
root# ps ax | grep mbd 14244 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/nmbd -D 14245 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/nmbd -D 14290 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/smbd -D $rootprompt; ps ax | grep winbind 14293 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/winbindd -B 14295 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/winbindd -B
The winbindd daemon is running in split mode (normal) so there are also two instances of it. For more information regarding winbindd, see TOSHARG, Chapter 22, Section 22.3. The single instance of smbd is normal.
Check that an anonymous connection can be made to the Samba server:
root# smbclient -L localhost -U% Sharename Type Comment --------- ---- ------- netlogon Disk Network Logon Service accounts Disk Accounting Files finsvcs Disk Financial Service Files IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba3) ADMIN$ IPC IPC Service (Samba3) hplj4 Printer Hewlett-Packard LaserJet 4 hplj6 Printer Hewlett-Packard LaserJet 6 qms Printer QMS Magicolor Laser Printer XXXX Server Comment --------- ------- SLEETH Samba 3.0.12 Workgroup Master --------- ------- BILLMORE SLEETHThis demonstrates that an anonymous listing of shares can be obtained. This is the equivalent of browsing the server from a Windows client to obtain a list of shares on the server. The -U% argument means, send a "NULL username and a NULL password."
Verify that the printers have the IP addresses assigned in the DHCP server configuration file. The easiest way to do this is to ping the printer name. Immediately after the ping response has been received, execute arp -a to find the MAC address of the printer that has responded. Now you can compare the IP address and the MAC address of the printer with the configuration information in the /etc/dhcpd.conf file. They should, of course, match. For example:
root# ping hplj4 PING hplj4 (192.168.1.11) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from hplj4 (192.168.1.11): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.113 ms root# arp -a hplj4 (192.168.1.11) at 08:00:46:7A:35:E4 [ether] on eth0
The MAC address 08:00:46:7A:35:E4 matches that specified for the IP address from which the printer has responded and with the entry for it in the /etc/dhcpd.conf file.
Make an authenticated connection to the server using the smbclient tool:
root# smbclient //sleeth/accounts -U alanm Password: XXXXXXX smb: \> dir . D 0 Sun Nov 9 01:28:34 2003 .. D 0 Sat Aug 16 17:24:26 2003 .mc DH 0 Sat Nov 8 21:57:38 2003 .qt DH 0 Fri Sep 5 00:48:25 2003 SMB D 0 Sun Oct 19 23:04:30 2003 Documents D 0 Sat Nov 1 00:31:51 2003 xpsp1a_en_x86.exe 131170400 Sun Nov 2 01:25:44 2003 65387 blocks of size 65536. 28590 blocks available smb: \> q
Procedure 3.3. Windows XP Professional Client Configuration
Configure clients to the network settings shown in ???. All clients use DHCP for TCP/IP protocol stack configuration. DHCP configures all Windows clients to use the WINS Server address 192.168.1.1.
Join the Windows Domain called BILLMORE. Use the Domain Administrator user name root and the SMB password you assigned to this account. A detailed step-by-step procedure for joining a Windows 200x/XP Professional client to a Windows Domain is given in ???. Reboot the machine as prompted and then logon using a Domain User account.
Verify on each client that the machine called SLEETH is visible in , that it is possible to connect to it and see the shares and , and that it is possible to open that share to reveal its contents.
Instruct all users to log onto the workstation using their assigned user name and password.
Install a printer on each using the following steps:
Click ->->+Add Printer+. Do not click . Ensure that is selected.
Click . In the panel labeled , select HP. In the panel, select the printer called HP LaserJet 4. Click .
In the panel labeled , select FILE:. Accept the default printer name by clicking . When asked, “Would you like to print a test page?”, click . Click .
You may be prompted for the name of a file to print to. If so, close the dialog panel. Right-click HP LaserJet 4->->->.
In the panel labeled , enter the name of the print queue on the Samba server as follows: \\SERVER\hplj4. Click + to complete the installation.
Repeat the printer installation steps above for the HP LaserJet 6 printer as well as for the QMS Magicolor XXXX laser printer.
As a network administrator, you already know how to create local machine accounts for Windows 200x/XP Professional systems. This is the preferred solution to provide continuity of work for notebook users so that absence from the office network environment does not become a barrier to productivity.
By creating a local machine account that has the same user name and password as you create for that user in the Windows Domain environment, the user can log onto the machine locally and still transparently access network resources as if logged onto the domain itself. There are some trade-offs that mean that as the network is more tightly secured it becomes necessary to modify Windows client configuration somewhat.
In this network design and implementation exercise, you have created a Windows NT4 style Domain Controller using Samba-3.0.12. As a result of following these guidelines meant that you experienced and implemented several important aspects of Windows networking. In the next chapter of this book, you build on the experience gained. These are the highlights from this chapter:
You implemented a DHCP Server and Microsoft Windows clients were able to obtain all necessary network configuration settings from this server.
You created a Windows Domain Controller. You were able to use the network logon service and successfully joined Windows 200x/XP Professional clients to the Domain.
You created raw print queues in the CUPS printing system. You maintained a simple printing system so that all users can share centrally managed printers. You installed native printer drivers on the Windows clients.
You experienced the benefits of centrally managed user accounts on the server.
You offered Mobile notebook users a solution that allows them to continue to work while away from the office and not connected to the corporate network.
Your new Domain Controller is ready to serve you. What does it mean? Here are some questions and answers that may help.
- 1. What is the key benefit of using DHCP to configure Windows client TCP/IP stacks?
- 2. Are there any DHCP server configuration parameters in the /etc/dhcpd.conf that should be noted in particular?
- 3. Is it possible to create a Windows Domain account that is specifically called Administrator?
- 4. Why is it necessary to give the Windows Domain Administrator a UNIX UID of 0?
- 5. One of my junior staff needs the ability to add machines to the Domain, but I do not want to give him root access. How can we do this?
- 6. Why must I map Windows Domain Groups to UNIX groups?
- 7. I deleted my root account and now I cannot add it back! What can I do?
- 8. When I run net groupmap list, it reports a group called Administrators as well as Domain Admins. What is the difference between them?
- 9. What is the effect of changing the name of a Samba server, or of changing the Domain name?
- 10. How can I manage user accounts from my Windows XP Professional workstation?